
Laptops have become an indispensable tool in our modern lives, serving various purposes ranging from work to entertainment. When choosing a laptop, one of the critical factors to consider is the display technology it utilizes. With a plethora of options available in the market, understanding the different laptop display technologies can help you make an informed decision. In this article, we will explore and compare various laptop display technologies, shedding light on their unique features, advantages, and drawbacks. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which display technology is the right fit for your needs.
Introduction
The display technology of a laptop plays a pivotal role in defining the visual experience it offers. It determines factors like image quality, color reproduction, contrast ratio, viewing angles, and more. By understanding the different display technologies available, you can choose a laptop that meets your specific requirements, whether it’s for professional tasks, multimedia consumption, or gaming.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)

LCD displays have been the standard in laptops for many years. They use liquid crystals to control the passage of light and create images. LCD panels offer good color reproduction and sharpness, making them suitable for most everyday tasks. However, they may have limited viewing angles and lower contrast ratios compared to other display technologies.
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) Displays

LED displays are an advancement over LCD technology. Instead of using fluorescent backlights, LED displays utilize energy-efficient light-emitting diodes. They offer improved brightness, better color accuracy, and higher contrast ratios. LED displays are widely used in modern laptops due to their superior performance and energy efficiency.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) Displays

OLED displays are known for their exceptional image quality and vibrant colors. Unlike LCD and LED displays, OLED panels do not require a backlight. Each pixel in an OLED display emits its light, resulting in true blacks, infinite contrast ratios, and wide color gamuts. OLED displays deliver stunning visuals, making them ideal for multimedia and content creation tasks. However, they can be more expensive and may suffer from burn-in issues with static images displayed for extended periods.
TN (Twisted Nematic) Panels
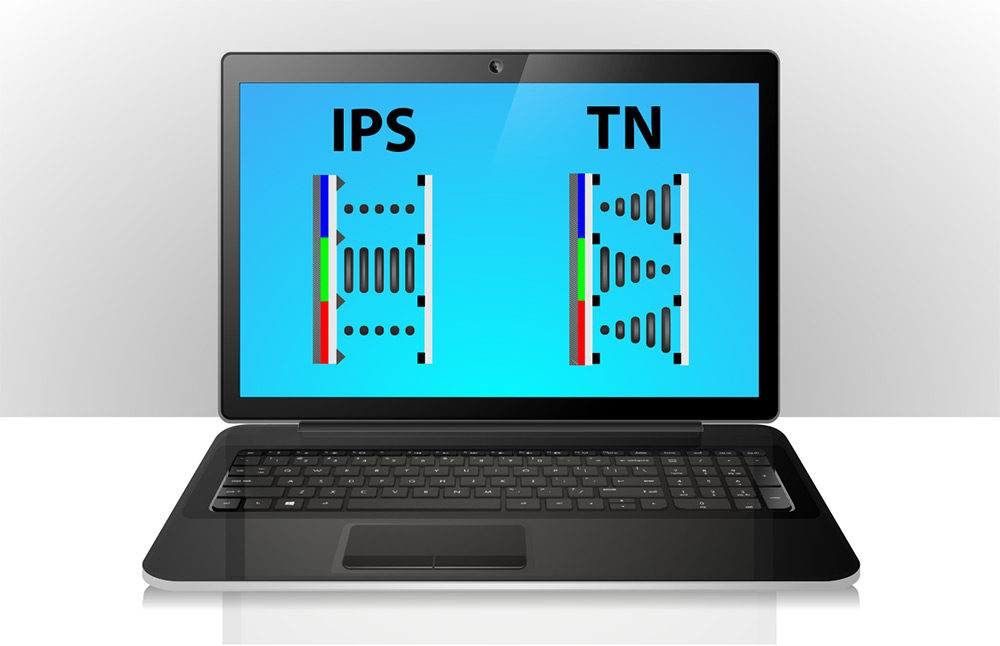
TN panels are another type of LCD technology commonly found in budget-friendly laptops and gaming displays. They offer fast response times, making them ideal for fast-paced gaming and reducing motion blur. However, TN panels often compromise on color accuracy and viewing angles, making them less suitable for tasks that require accurate color representation.
HDR (High Dynamic Range) Displays
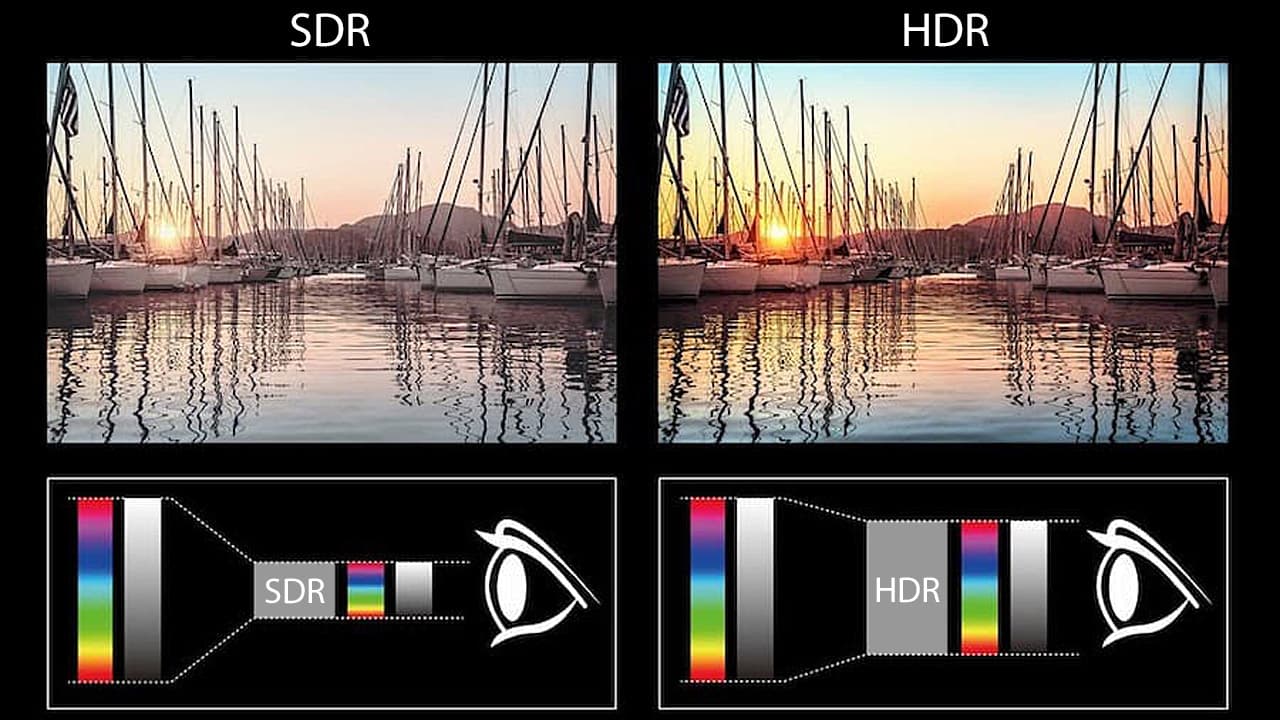
HDR displays are designed to deliver a broader range of colors and increased contrast ratios. They enhance the visual experience by providing more detail in both bright and dark areas of an image. HDR displays offer a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience, but it’s important to ensure that the content you consume supports HDR to fully benefit from this technology.
Touchscreen Displays

Touchscreen displays have gained popularity due to their intuitive interaction capabilities. They allow you to directly interact with the screen using gestures, taps, and swipes, providing a more versatile computing experience. Touchscreen laptops are especially useful for tasks like drawing, note-taking, and navigating touch-optimized applications. However, they may add additional weight and glare to the display.
Screen Resolution HD, Full HD, and Beyond

Screen resolution refers to the number of pixels a display can show, determining the level of detail and sharpness. HD (High Definition) and Full HD (Full High Definition) are common resolutions found in laptops. However, there are higher resolutions available, such as QHD (Quad High Definition) and 4K UHD (Ultra High Definition), which offer even more precise visuals. Choosing the right screen resolution depends on your usage requirements and budget.
Viewing Angles and Anti-Glare Technology

Viewing angles determine how well the display maintains its image quality when viewed from different angles. Wide viewing angles ensure consistent colors and contrast, even when viewing the screen from the sides. Anti-glare technology reduces reflections and glare, improving visibility in brightly lit environments. If you often collaborate or share your screen, a laptop with wide viewing angles and anti-glare technology can enhance the viewing experience for everyone involved.
Conclusion
Choosing the right laptop display technology is essential to ensure an optimal visual experience that aligns with your specific needs. Consider factors like LCD, LED, OLED, IPS, TN panels, HDR support, touchscreen capabilities, screen resolution, display size, refresh rate, color accuracy, viewing angles, and energy efficiency. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technology, you can make an informed decision that enhances your productivity, creativity, and entertainment.